
First off. As Functional Nutrition providers, it is fundamentally important to acknowledge that nutrient dense foods are the only true source of nutrition. Humans were designed to eat real food – not inject artificial substitutes directly into the blood stream.
The 14 healthy societies Dr. Weston A Price studied never injected synthetic vitamins into the blood stream.
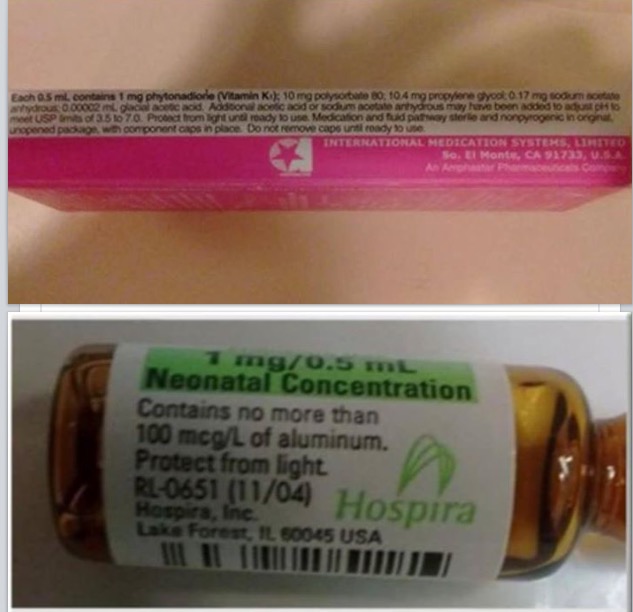
Furthermore, synthetic vitamin manufacturers package injectable or IV infused vitamins with added emulsifiers and preservatives that may have potentially harmful long term effects. For example, the Hospira Vitamin K shot that is offered at hospitals contain 2 ingredients that should never been combined, polysorbate 80 and aluminum.
Polysorbate 80 is known to open the blood brain barrier.(1,2) Aluminum is a known neurotoxin (3,4,5,6,7,8).
Here are the ingredients to the Vitamin K shot.
- 1mg phytonadiole (synthetic Vitamin K1 made from coal tar)
- 10mg of Polysorbate 80
- 100mcg/L of aluminum.
- 10.4mg of propylene glycol
- 0.17mg sodium acetate anhydrous
- 0.0002mL glacial acetic acid
How do hospital doctors guarantee the aluminum never enters the brain after a one day old receives a Vitamin K shot?
What are in all the other childhood injections? Can the Hepatitis B vaccine and the Vitamin K shot potentially cause harm, especially since they are both administered on day 1 of birth?
Aluminum is also in the Hepatitis B vaccine. Be sure to refer to the Vaccine Adjuvant Worksheet and point out to your parents where the neurotoxic heavy metals and polysorbate 80 are. Here’s a hint. Nearly all vaccines contain them.

Friendly reminder to your parents as you share this new information with them, “Every parent is doing the best with what they know.”
Now that they know more, it’s time to do better. Our kids are counting on it.

References:
1. Zhao YM, Xia AX, Wei YH, Ruan YP, Li FZ. [Polysorbate-80 modified neurotoxin nanoparticle with its transport and cytotoxicity against blood-brain barrier]. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2010 Oct;45(10):1312-6. Chinese. PubMed PMID: 21348312.
2. Ema M, Hara H, Matsumoto M, Hirata-Koizumi M, Hirose A, Kamata E. Evaluation of developmental neurotoxicity of polysorbate 80 in rats. Reprod Toxicol. 2008 Jan;25(1):89-99. Epub 2007 Aug 25. PubMed PMID: 17961976.
3. Murphy CP, Cox RL, Harden EA, Stevens DA, Heye MM, Herzig RH. Encephalopathy and seizures induced by intravesical alum irrigations. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1992 Oct;10(4):383-5.
4. Reusche E, Pilz P, Oberascher G, Lindner B, Egensperger R, Gloeckner K, Trinka E, Iglseder B. Subacute fatal aluminum encephalopathy after reconstructive otoneurosurgery: a case report. Hum Pathol. 2001 Oct;32(10):1136-40.
5. Bishop NJ, Morley R, Day JP, Lucas A. Aluminum neurotoxicity in preterm infants receiving intravenous-feeding solutions. N Engl J Med. 1997 May 29;336(22):1557-61.
6. Crapper DR, Tomko GJ. Neuronal correlates of an encephalopathy associated with aluminum neurofibrillary degeneration. Brain Res. 1975 Oct 31;97(2):253-64.
7. Crapper DR, Krishnan SS, Quittkat S. Aluminium, neurofibrillary degeneration and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 1976 Mar;99(1):67-80.
8. Gorell JM, Rybicki BA, Cole Johnson C, Peterson EL. Occupational metal exposures and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroepidemiology. 1999;18(6):303-8.

